The routing pipeline
Traffic in the system is routed according to the principle of a routing pipeline.
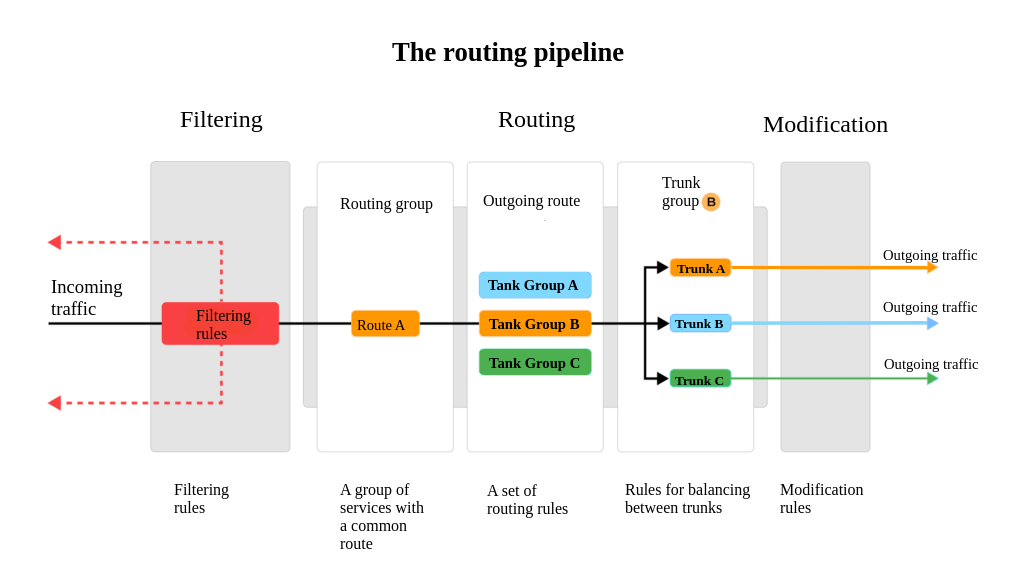
The pipeline approach assumes that all traffic from the customer to the supplier passes through a unified chain of administered processes:
- Filtration stage;
- Routing stage;
- Modification stage.
Each of these generalized stages at the interface level consists of a number of internally administered (configurable) components, which provides a flexible, fault-tolerant and transparent mechanism for passing traffic from the client to the provider through applications and services.
Filtering stage
The first stage is to process incoming traffic — filtering. This is an administrator-configurable mechanism for blocking client traffic that does not meet the specified characteristics. By default, the services connected to contractors do not contain any filtering components. This means that the system will skip all incoming traffic without processing.
The filtering mechanism has an architecture based on creating a set of filtering rules. The rules are contained inside Filters — universal (not tied to any customer) sets of filtering rules.
Filters are created and stored in the Filters section.
The created filters are linked as a configuration component to a specific service of a particular customer:

Routing stage
Determining the name of the provider and selecting the trunk to which the last stage of traffic filtering will be sent is the result of the second stage of the routing pipeline.
To implement this stage, the following components are administered:
- Outgoing routing groups;
- Outgoing routes;
- Trunk groups;
- Trunks.
After the system has filtered the traffic that entered it, it accesses the Outgoing Routing Group set for the service, which contains the Outgoing route.
Outgoing routing groups are created and stored in the Outgoing Routing Groups section.
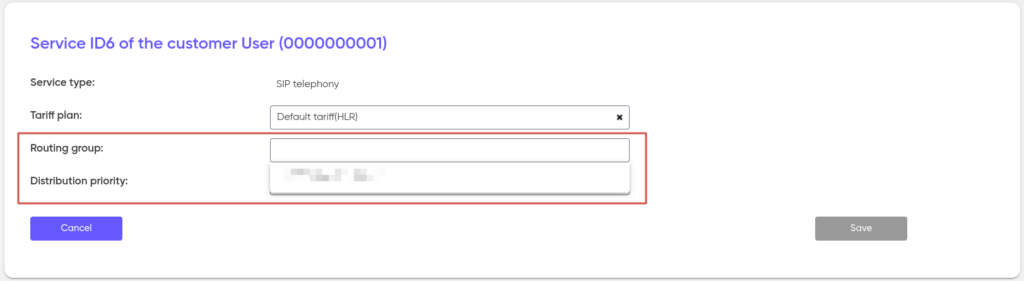
The outgoing routing groups mechanism allows you to centrally change the outgoing route for all services that specify this group. In order to change the route for a group of services, it is enough to reassign the route in the group settings.
A route is a set of rules that, depending on the nature of the traffic and on the specified rule, allow you to determine the trunk group of the provider.
Modifiers are created and stored in the Outgoing Routes section.
A Trunk group is an association of several trunks, with an established option for distributing (balancing) traffic between them (a type of trunk group).
Trunk groups are assigned according to routing rules.

Trunk groups are created and stored in the Trunk Group section.
Modification stage
After the supplier is determined at the routing stage, we can use the administered rules to modify the traffic before sending in such a way that it meets the requirements of the supplier. Modificators are responsible for this stage of the routing pipeline.
Modifiers are created and stored in the Modificators section.
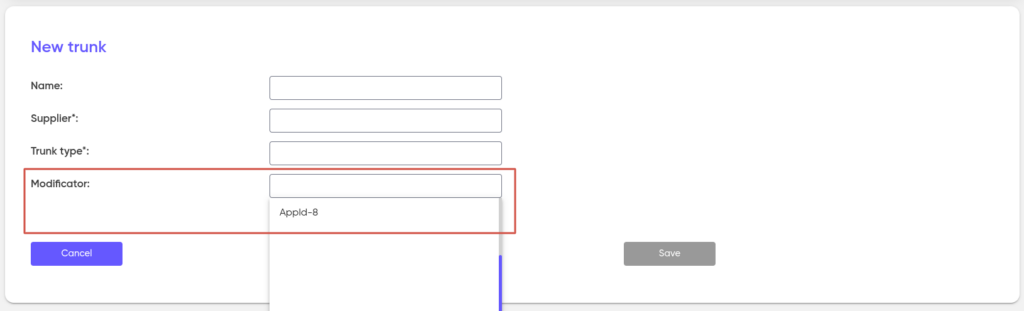
After the Modificator is created, it is assigned to the Provider trunks.